What is edge computing?
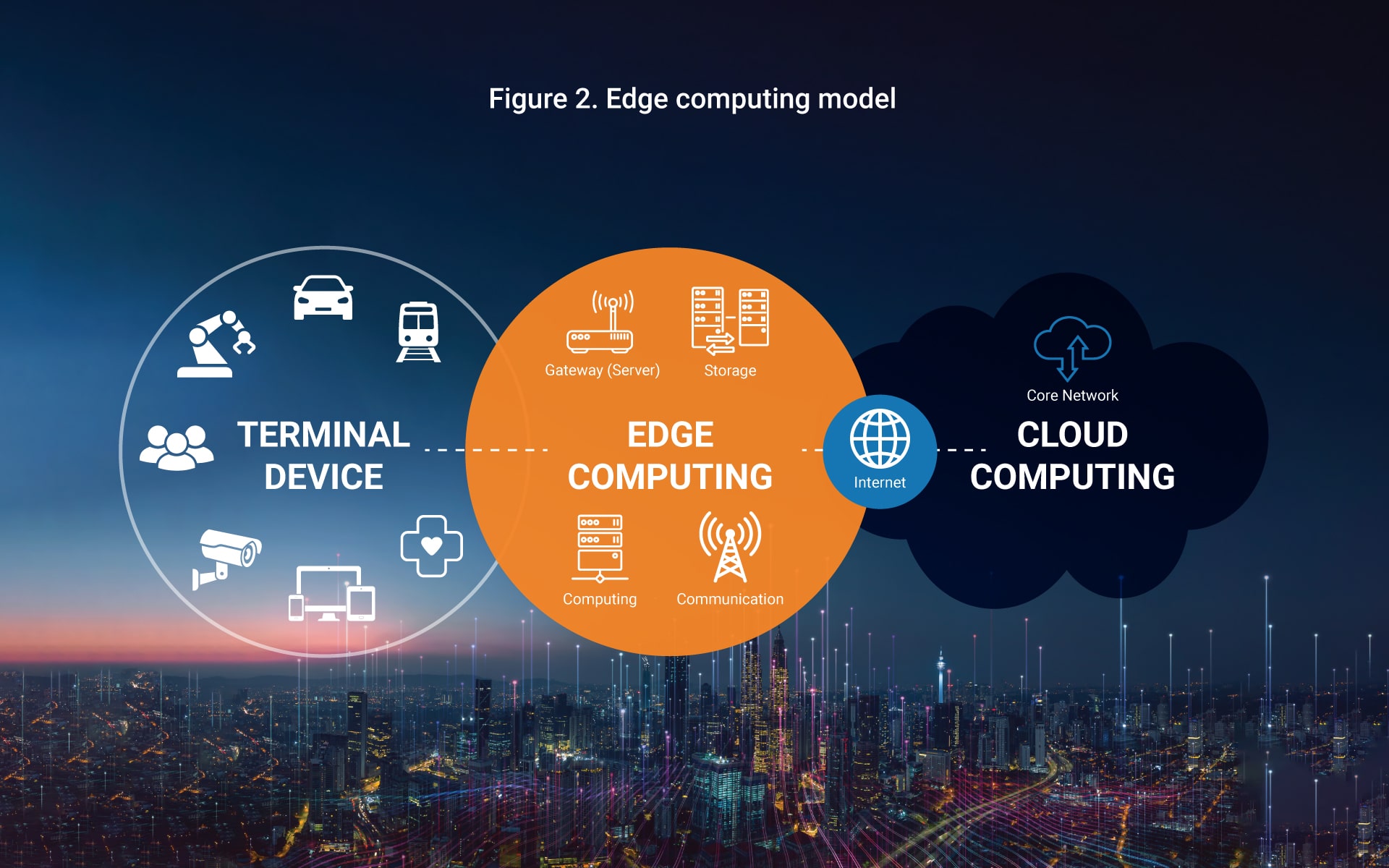
Having access to relevant data, and the valuable insights that it contains, is critical for companies of all sizes and industries. Edge computing is a distributed IT architecture in which user data is processed at the periphery of the network on so-called “edge devices,” which are physically located as close to the original data source as possible.
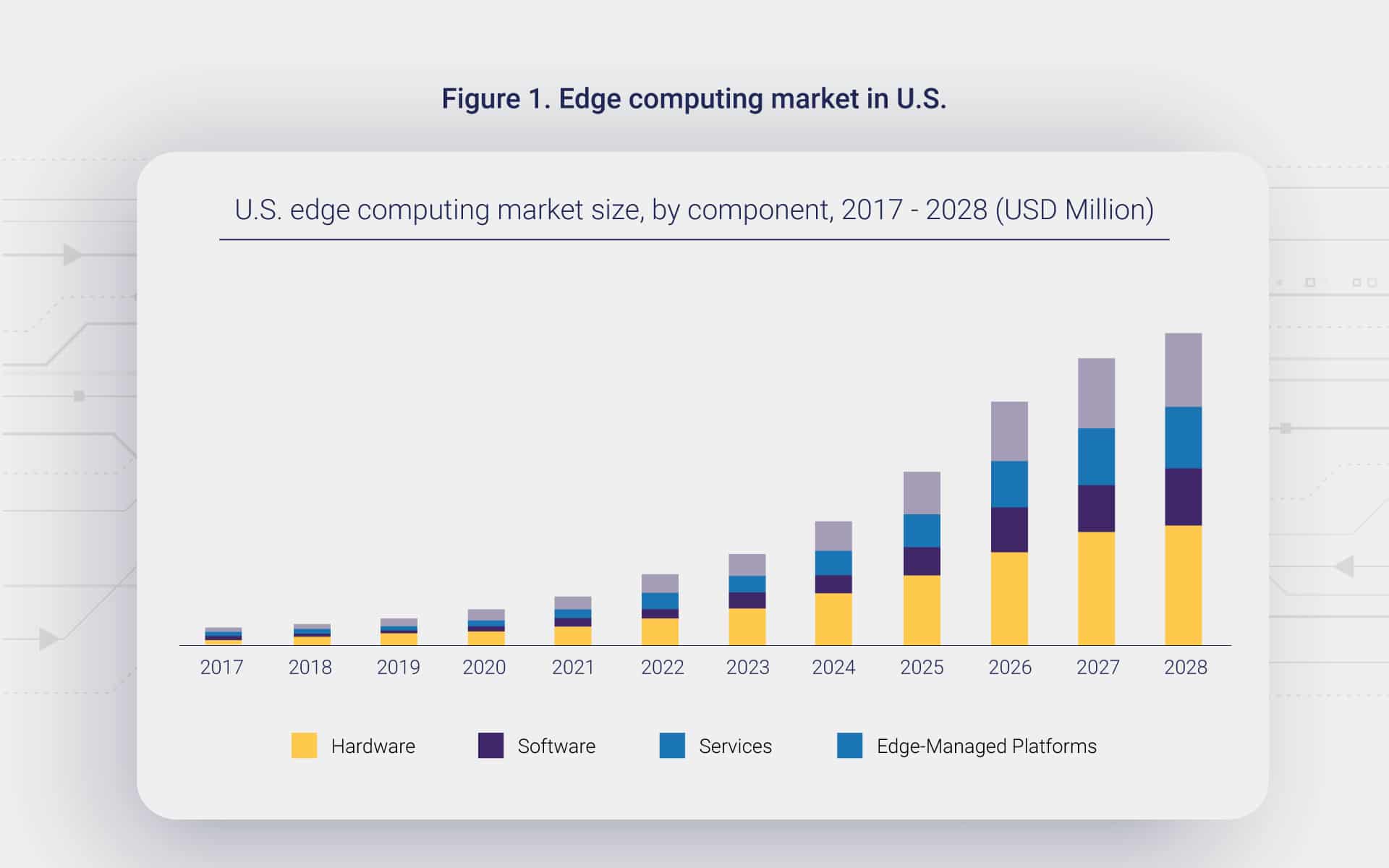
In recent years, edge computing has soared in popularity. According to Grand View Research, the edge computing market was valued at $4.68 billion in 2020, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.4 percent from 2021 to 2028.
Why has edge computing seen such an explosion of interest? Today’s businesses are scattered across multiple sites, from offices and warehouses to factories and construction sites. This has led to the desire to collect vast amounts of data from sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, operating in real-time from remote locations.
Edge computing is especially crucial for companies seeking a competitive advantage over their business rivals. For example, edge computing can help reduce IT costs because you no longer need to transfer all of your IoT data to the cloud or keep it on-premises. Instead, edge analytics tools can sift through the noise and identify which of this data is most valuable for in-depth analysis. High-value data can also be compressed at the edge, further reducing the overall data volume and network bandwidth that’s needed to move data to the cloud.
As a relatively new technology trend, however, edge computing entails a great deal of business complexity. Moving computation to the edge requires major adjustments to your IT infrastructure, including connectivity, application development, traffic delivery, and service management. In particular, businesses need storage solutions that can address the unique challenges of edge computing, as we’ll discuss later.
What are the use cases of edge computing?
There are as many possible use cases and applications for edge computing as there are businesses that want to adopt it. In this section, we’ll offer just a few ideas for how to use edge computing.
Edge computing for factory automation
One of the most popular edge computing use cases is on the factory floor. Below are just a few examples:
-
-
- On-site production line monitoring: Edge devices equipped with an AI inference system can use IP cameras to monitor operators’ actions on the factory floor, identifying any abnormal behavior and reporting it to the relevant managers.
- Automatic machine monitoring: Edge devices can offer real-time insights into the operating status of factory equipment, easing the data collection process with an edge-to-cloud integrated system. The insights from these devices can help realize more efficient production processes, reduce maintenance costs, and implement better employee training programs.
- Electronic component production inspection: Using AI image processing technology, edge devices can recognize anomalies on complex electronic parts and surfaces. These capabilities help improve manufacturing efficiency and quality control while saving human employees a great deal of tedious manual labor.
-
Edge computing for factory automation
Public transportation will be essential to the growth of the “smart city,” and edge computing can lead the way. Buses and trains equipped with edge devices can help provide drivers and passengers with valuable information, such as detecting a door’s open/close status and providing real-time monitoring of driving conditions.
Edge computing for healthcare
Artificial intelligence, big data, and edge computing can help improve public health, such as managing the spread of COVID-19. For example, edge technology can automatically detect symptoms such as high body temperature, or analyze images and videos to assess workers’ compliance with wearing face masks or other PPA (personal protective equipment). Using edge computing for healthcare can reduce human error and dramatically improve speed and efficiency.
Edge computing for energy
Mining takes place in hostile environments, making 24/7 human surveillance impractical. This leads to the need for remote monitoring systems that can detect dangerous conditions, such as a collapse or the presence of unauthorized individuals. Edge computing facilitates real-time, on-site security and helps keep workers safe.
What are the challenges of storage for edge computing?
Edge computing faces unique and unexpected challenges that are markedly different from those of the traditional data center. The potential difficulties of storage devices for edge computing include:
-
- Environmental hazards: Edge devices can be deployed anywhere from blazing-hot deserts to freezing-cold snowscapes. Unlike the predictable environment of a server farm, edge storage devices must be built to endure and withstand dramatic changes in temperature and weather.
- Stable performance: Beyond the environment, edge storage devices also need to keep up with vast quantities of real-time streaming data sources. Modern use cases of edge computing require these devices to exhibit stable, consistent performance while constantly monitoring, processing, and analyzing new information.
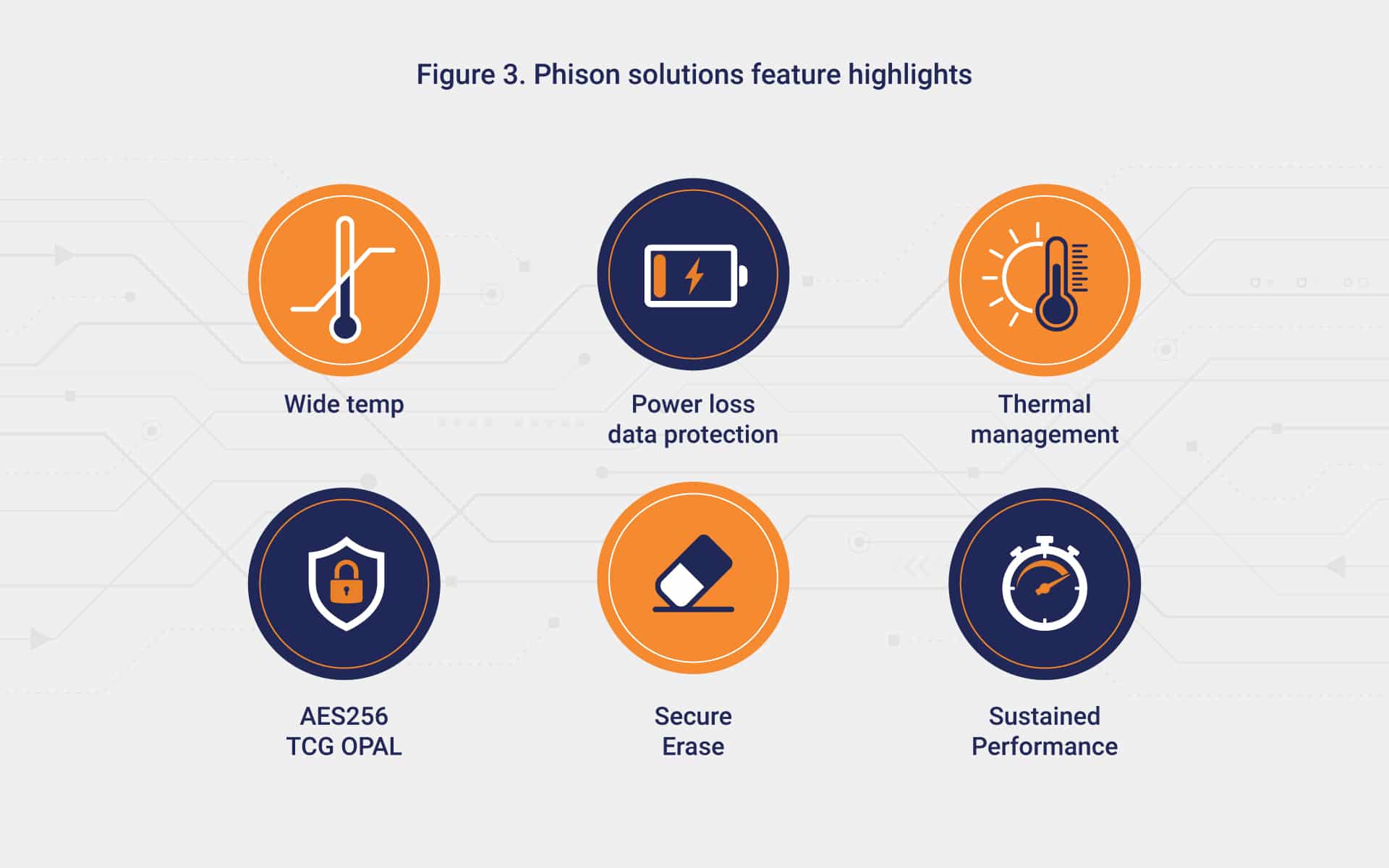
- Data protection: Keeping data safe at the edge is a preeminent concern since new information doesn’t automatically join your IT ecosystem. Edge storage devices should be equipped with technologies for thermal management, protection against sudden power loss, data encryption, and more.
Heading to the edge with Phison
Edge computing enhances operational efficiency, avoids unplanned downtime, and enables faster innovation—but it also requires strong technical expertise to do it right. Phison is committed to solving the challenges of edge devices and helping our clients fulfill their edge computing initiatives for digital transformation.
Whatever your edge computing pain point, Phison has the storage solution to match.
Our industry-leading storage devices have been custom-built with features for your edge computing needs: wide temperature support, power loss protection, security, and more. To learn how Phison can help with your edge computing project, check out the latest news and articles on the Phison blog, or contact us today for a chat about your business goals and requirements.
Resources used in this article:
1. Tech Target
2. SAS Insights
3. Grand View Research
4 ADVANTECH